Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of The Service Design Of The Service Lifecycle
ITIL Service Blueprint
From It Procedure Wiki
![]()
Objective: The objective of ITIL Service Design is to design new IT services. The scope of the Service Design lifecycle stage includes the design of new services, also as changes and improvements to existing ones.
Role of: IT Service Management | ITIL processes
Processes: ITIL Service Design
Service Design identifies service requirements and devises new service offerings also every bit changes and improvements to existing ones.

The ITIL service lifecycle stage of Service Design (encounter fig. 1) includes the following master processes :
- Design Coordination
- Procedure Objective: To coordinate all service design activities, processes and resources. Design coordination ensures the consequent and effective blueprint of new or changed It services, service management data systems, architectures, engineering, processes, information and metrics.
- Service Catalogue Management (SCM)
- Process Objective: To ensure that a Service Catalogue is produced and maintained, containing authentic data on all operational services and those being prepared to be run operationally. Service Catalogue Management provides vital information for all other Service Management processes: Service details, electric current status and the services' interdependencies.
- Service Level Management (SLM)
- Process Objective: To negotiate Service Level Agreements with the customers and to design services in accordance with the agreed service level targets. Service Level Management is also responsible for ensuring that all Operational Level Agreements and Underpinning Contracts are advisable, and to monitor and report on service levels.
- Adventure Management
- Process Objective: To identify, assess and control risks. This includes analyzing the value of avails to the business, identifying threats to those avails, and evaluating how vulnerable each asset is to those threats.
- Chapters Management
- Process Objective: To ensure that the chapters of Information technology services and the It infrastructure is able to deliver the agreed service level targets in a cost effective and timely fashion. Capacity Management considers all resources required to deliver the IT service, and plans for short, medium and long term business requirements.
- Availability Direction
- Process Objective: To define, analyze, plan, measure and meliorate all aspects of the availability of Information technology services. Availability Management is responsible for ensuring that all IT infrastructure, processes, tools, roles etc. are advisable for the agreed availability targets.
- IT Service Continuity Direction (ITSCM)
- Process Objective: To manage risks that could seriously impact IT services. ITSCM ensures that the IT service provider tin always provide minimum agreed Service Levels, by reducing the risk from disaster events to an acceptable level and planning for the recovery of It services. ITSCM should be designed to back up Business Continuity Management.
- Data Security Management
- Process Objective: To ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of an organization's data, data and IT services. Information Security Direction usually forms office of an organizational approach to security management which has a wider scope than the IT Service Provider.
- Compliance Direction
- Procedure Objective: To ensure It services, processes and systems comply with enterprise policies and legal requirements.
- Compages Management
- Process Objective: To define a design for the future development of the technological mural, taking into account the service strategy and newly available technologies.
- Supplier Management
- Process Objective: To ensure that all contracts with suppliers support the needs of the business, and that all suppliers meet their contractual commitments.
ITIL 4 Service Blueprint
The Service Pattern processes described here (fig. 1) follow the specifications of ITIL V3, where Service Blueprint is the second stage in the Service Lifecycle.
ITIL V4 has moved from the Service Lifecycle concept to a more holistic arroyo that includes key concepts, the Iv Dimensions Model and the Service Value Organization (SVS)
Instead of processes, ITIL 4 describes 34 'practices', and many of the 26 processes specified in ITIL V3 can exist found in ITIL four equally practices.
ITIL 4 therefore refers to Service Blueprint as a practise and describes Service Design key concepts. In addition, ITIL 4 includes some practices that correspond to ITIL V3 Service Blueprint processes, such every bit Service Level Management and Service Catalogue Direction.
The shift from processes to practices means ITIL V4 is no longer prescriptive about processes and gives organizations more than freedom to define tailor-made Service Design processes.
Since the processes specified in ITIL V3 have not been invalidated with the introduction of ITIL V4, organizations that need to define their Service Design processes can withal use the processes specified in ITIL V3 as templates.
KPIs | Templates | Roles
- KPIs for Service Design
- Service Design templates and checklists
- ITIL roles inside Service Design
Downloads
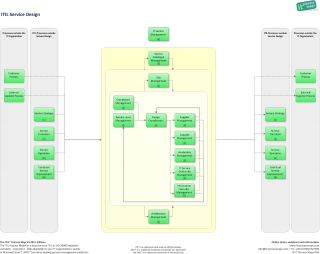
The ITIL discipline Service Design at a glance
Use the following links to open the process overview of Service Design showing the most of import interfaces:
- ITIL Service Design (.JPG)
- ITIL Service Design (.PDF)
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
ITIL iv Service Blueprint › Pattern Coordination › Service Catalogue Mgmt. › SLM › Risk Mgmt. › Capacity Mgmt. › [...] › Supplier Mgmt.
Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of The Service Design Of The Service Lifecycle,
Source: https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/ITIL_Service_Design
Posted by: williamswifigh75.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of The Service Design Of The Service Lifecycle"
Post a Comment